A surgical navigation system is a medical equipment that allows visualizing the anatomy of the patient during a surgical procedure and accurately tracking the location of the surgical instruments used. The use of these equipment during different surgical procedures provides greater precision, the performance of less invasive procedures and helps to obtain better surgical results.
These medical devices allow precise planning and execution of surgical procedures in operating rooms, that is to say, they allow guiding surgical instruments such as electroscalpel. They are composed of a series of instruments that are connected to screens by sensors with imaging methods.
What benefits does a surgical navigation system offer?
Today, thanks to technological development, surgical navigation systems provide optical tracking capabilities as well as integration with external devices such as microscopes and ultrasounds. They are the accepted standard for neurosurgeries and have the ability to monitor a large number of instruments simultaneously.
Among the many benefits of using surgical navigation systems are:
- Lower number of post-surgical complications (infections, fistulas, among others).
- Reduced risk of sequelae
- Shorten the hospital stay.
- Its use generates smaller and more aesthetic incisions.
Applications where surgical navigation systems are used
The use of surgical navigation systems are highly complex and technologically demanding, so it is necessary to have a multidisciplinary team that is well trained and trained to work with this useful tool. Among the procedures where optical surgical navigation systems can be used we have:
- Biopsy.
- Catheter placement.
- Tumor resection.
- Decompression of the column.
- Pelvic or spinal fixation.
- Treatment for spinal or sacral trauma.
- Deep brain stimulation electrode positioning.
How does a surgical navigation system work?
A surgical navigation system is based on the principle of high-precision stereoscopic vision. Currently these equipment generally include polaris navigation systems, micron navigation and others, and have become an integral part of computer-assisted surgery, this has allowed the use of digital images in surgical procedures that gives surgeons the opportunity to perform preoperative planning and precise use of instruments during the intervention.
These surgical navigation systems have as their main function to help accurately locate anatomical structures in open or percutaneous procedures. In this sense, surgical navigation systems work with conventional imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI scans.
What do we offer you in Kalstein?
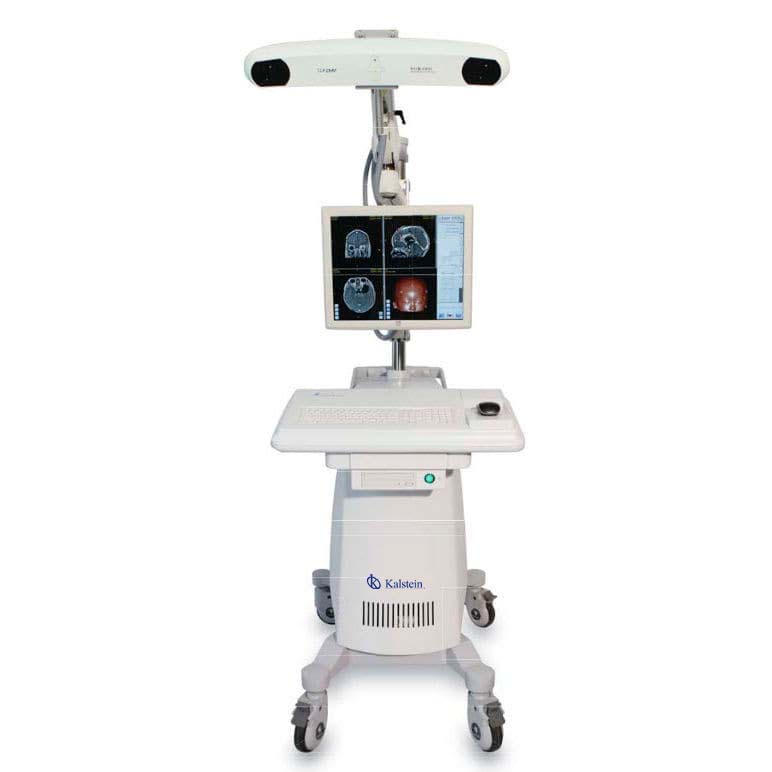
Kalstein is a company MANUFACTURER of medical and laboratory equipment of the highest quality and that have the most advanced technology at the best prices in the market, so we guarantee you a safe and effective purchase, knowing that you have the service of a solid company and committed to health. In this opportunity we present our innovative YR02143 electromagnetic navigation system assisted by computer, which has the following features: HERE
- It is widely used for surgical visualization, planning and navigation to help minimize iatrogenic trauma to surrounding brain tissue and reduce the risk of surgical complications in cranial procedures (such as cranial neurology and ENT surgery).
- The advanced optical tracking system tracks real-time 3D position and orientation of active or passive markers attached to surgical tools, for exceptional accuracy (1.0 mm spatial resolution) and reliability.
- The method of 3D simulation and modeling of anatomical structures in material (such as skin, skull, brain tissue or target injury) can be easily defined by surgical convenience.
- With the navigation probe and advanced optical measurement technology built in, the surgeon can easily quantify the size and position of the lesions, then scientifically design the surgical approach.
- The system provides operators with four navigation modes for comprehensive monitoring of the navigation process.
- The intelligent software will help calibrate and compensate for unexpected changes in anatomical structure and brain change induced by removal of the intracranial lesion area.
For more information we invite you to take a look at: HERE