Horizontal and Vertical Electrophoresis: Differences
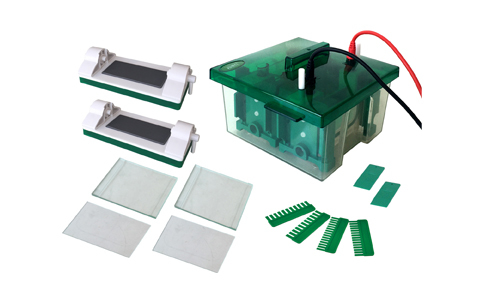
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used in genetics to separate mixtures containing DNA, RNA and other proteins according to their respective molecular charge and size. The DNA, RNA, or proteins to be separated in this method are executed through a gel containing small pores. The molecules are conducted through the gel by an electric field.
Multiple myeloma and protein electrophoresis
Multiple Myeloma is a multifocal plasma cell neoplasm that affects the bone marrow and is associated with the production of a serum and urine monoclonal protein. The cause is progressive unregulated proliferation of plasma cells that accumulate in the bone marrow. These cells secrete immunoglobulin (Ig) excessively; typically: IgG 57%, IgA 21%, IgD 1%, IgM, IgE, only rarely in 18% of cases of light chains alone. Proliferation of multiple myeloma interferes with the normal production of cells in the bone marrow and typically results in anemia. Leukopenia and thrombocytopenia occasionally occur. Another feature is that multiple myeloma cells secrete certain osteoclast-stimulating and osteoblast-inhibiting substances that result in exaggerated destruction of bone tissue with subsequent pathologic fracture, in many cases hypercalcemia.
What are the principles of electrophoresis?
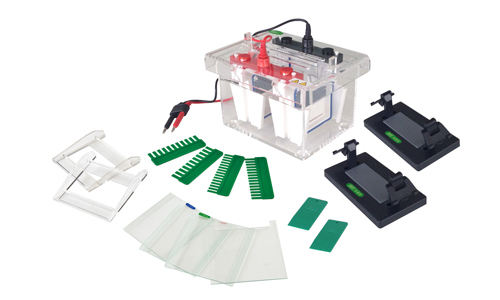
This technique is widely used in laboratories, especially in those of molecular biology, because it is used in important procedures such as separation, analysis and purification of RNA, DNA, or proteins, nucleic acids, this process is done because most of the biomolecules have an electric charge where its magnitude depends on the pH of the environment in which they are, because of this the biomolecules move when they undergo an electric field to the charge pole opposite the molecule.
Electrophoresis chamber

The electrophoresis chamber is the device in which the sample is introduced for this process, and where the electromagnetic field that is formed in the electrophoresis process is created, it takes place within a buffer solution in which the gel is immersed; the high concentration of electrolytes makes possible the transition of the electrical current. The principle of electrophoresis consists in the migration of molecules through the gel generated by the electromagnetic field according to the molecular weight and size. The gel has pores that act as a colator, causing small molecules to move faster than large molecules. In the chamber there are two poles that connect to the power source.
How does electrophoresis work?
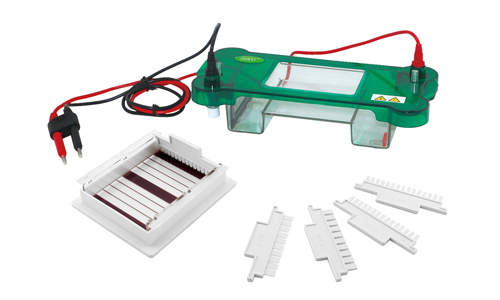
Electrophoresis is an analytical method in which a controlled electric current is used to separate biomolecules according to their size-to-electric charge ratio, using a jellylike matrix as the base. When a mixture of ionized and net charged molecules are positioned in an electric field, they undergo an attraction force toward the pole with opposite charge, allowing time elapse the positively charged molecules move toward the cathode (negative pole) and those charged positively move toward the anode (positive pole).
What is electrophoresis?

Electrophoresis is an analytical method in which a controlled electric current is used in order to separate biomolecules according to their size-to-electric charge ratio, using a jellylike matrix as the basis. This technique has a variety of practical uses, including forensic medicine for human identification, the human genome project, research for proteins and genetic mutations, and clinical diagnostic tests.
What is the function of an operating table?
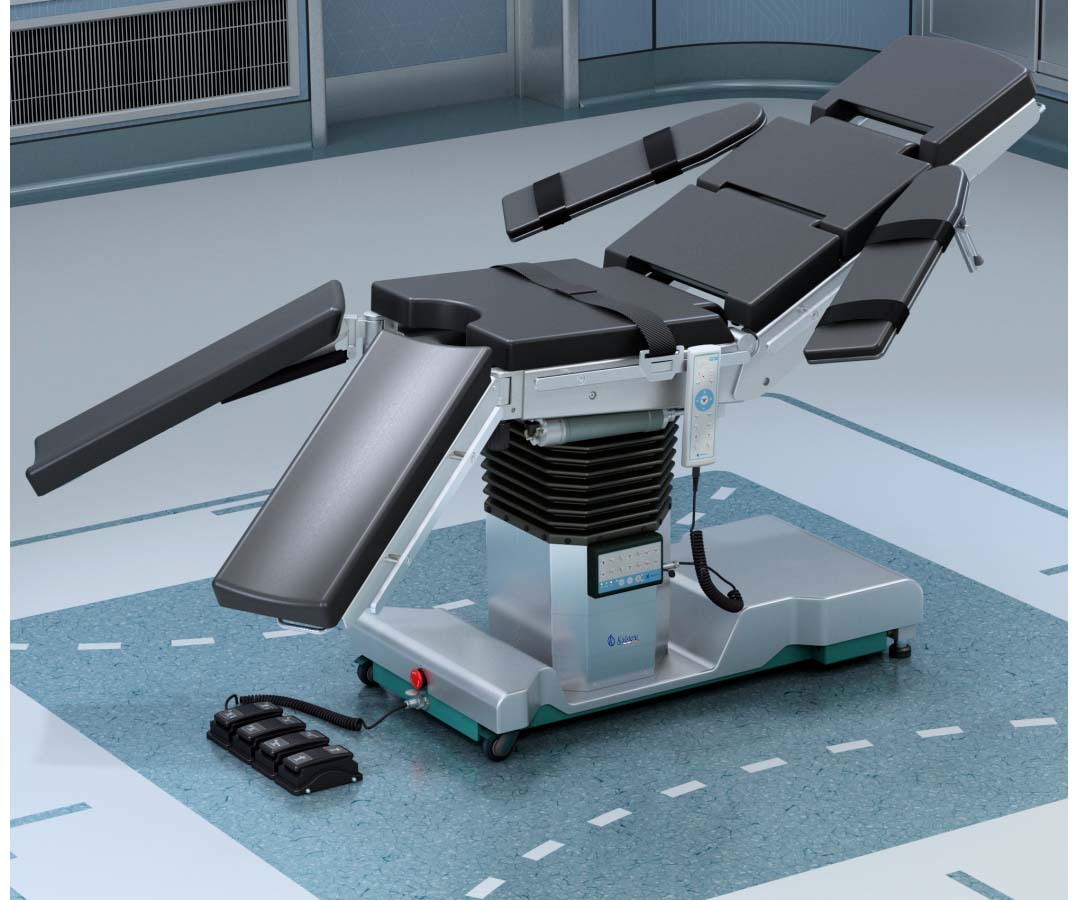

An operating table is a medical team that meets a series of precise rules, whose function is to position the patient during a surgical procedure, it has specific standards for the desired clinical position. It consists of a platform divided into sections, where the patient can sit or lie down. It also has arms; a remote control that adjusts the patient’s positions relative to the surgeon, table tilt and height; and other accessories that contribute to the stability of each position.
Types of operations and application tables
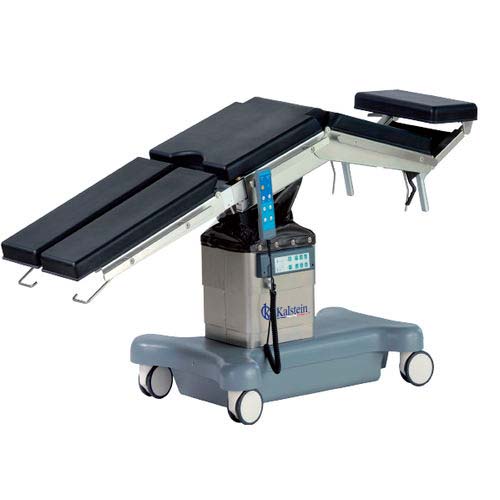

Operating tables are specialized operating tables used in operating rooms to position the patient during a surgical procedure, facilitating patient positioning during the various surgical procedures and allowing the surgeon good access to the surgical field.
Parts of an operating table

Operating tables, also called surgical tables, are used in the operating room to position patients during surgery. They consist of a main platform, on which the patient can sit or lie down and which can be divided into several sections
How do you split an operating table?

Operating tables, are used in all hospital units and are designed basically to exercise comfort to the patient, it is composed of a column, the top and the transporter, these tables can also be used for other specialized disciplines.
