Neo-Natal Incubator And Different Types Of Phototherapy
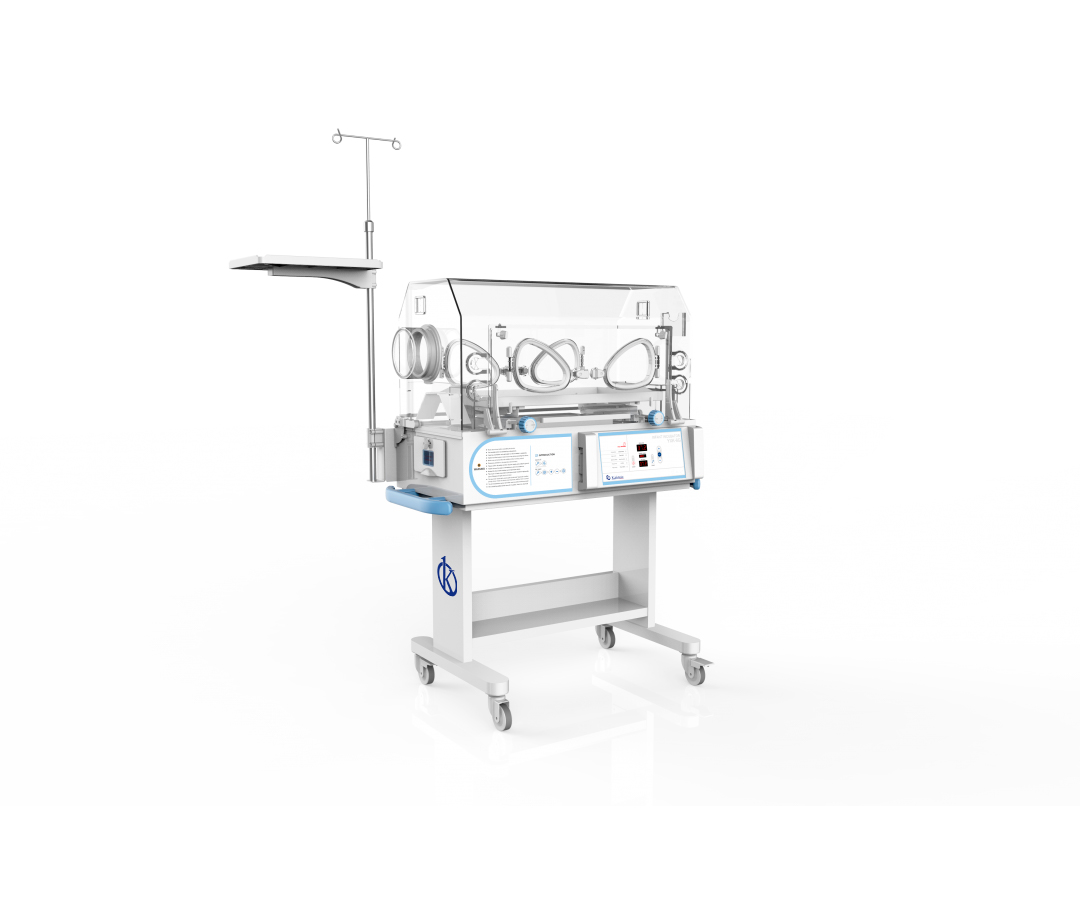

This type of device is intended to offer the full-term or premature newborn a warm and safe environment, where its vital signs can be monitored, to maintain a temperature that keeps it stable; in some cases when the blood of the baby and the mother are different, jaundice occurs in the newborn, needing special attention, through phototherapy, and all KALSTEIN incubators are conditioned for this.
What Does a Neonatal Incubator Do?
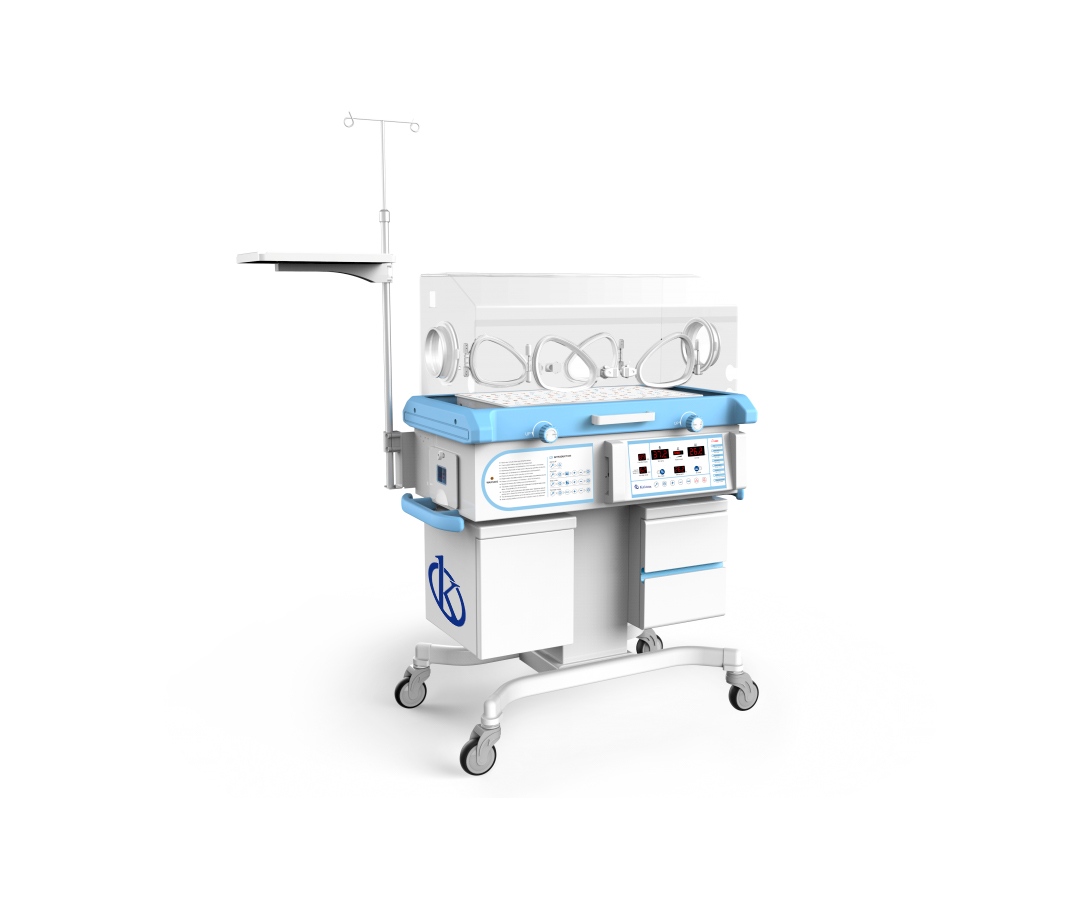
Neonatal incubators provide the newborn with a flow of hot air, through a fan or a turbine that takes it from the outside and passes it through a temperature measuring device, passing over a water tank used to moisten the air towards the patient. It is composed of the compartment for the neonate, transparent walls, mattress, platform, rolling base and control module, where all the parameters that will control the temperature are located.
Neonatal incubator with phototherapy
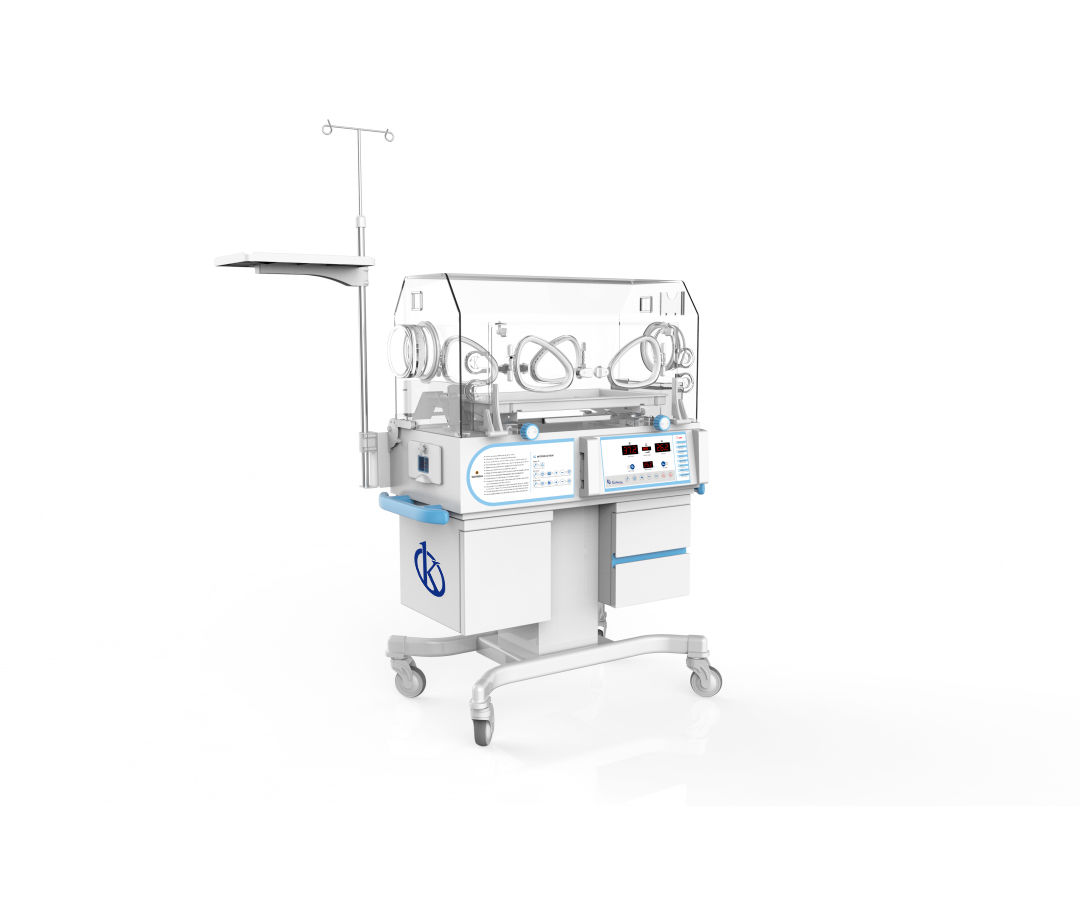
The neonatal incubator with phototherapy lamp is a device used to give life support, isolate and provide warmth to the newborn. In addition to providing optimal conditions for the care of neonates who are not prepared for extrauterine life, this type of incubator specializes in the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia in neonatal patients with jaundice.
How is a phototherapy incubator used?
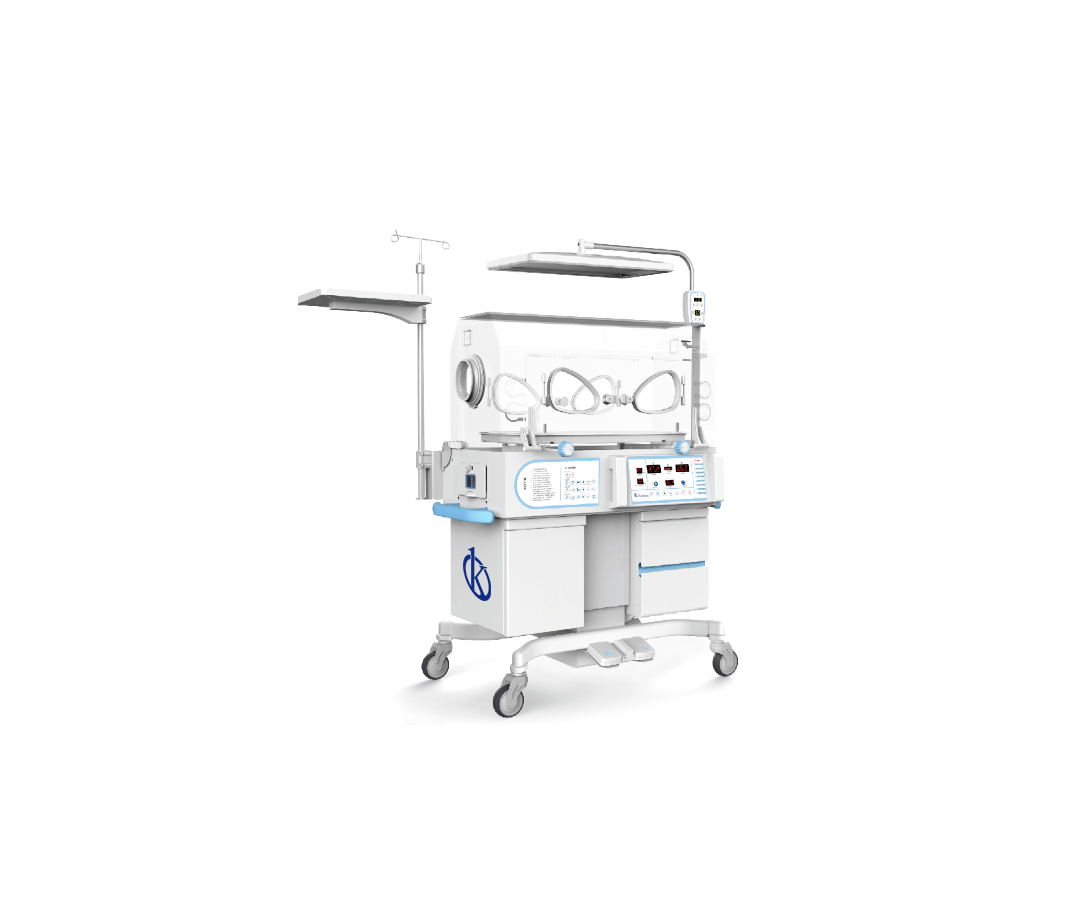
A phototherapy incubator is a specialized medical team that provides optimal conditions for the care of newborns who are not prepared for extrauterine life, and who suffer neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, clinical picture that leads to a condition known neonatal jaundice. This type of incubators have units of phototherapies, equipment composed by specialized lamps that allow to apply light therapy to treat hyperbilirubinemia, in addition to provide life support, isolate and provide heat to newborns.
Photo therapy incubators and neonatal jaundice

The phototherapy incubators are medical equipment used to provide a controlled environment to newborns, whether premature or full term, to undergo phototherapy, a therapeutic measure in which light emitted by special lamps is used to treat childhood jaundice, and thus reduce the effects of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
Infant heater and infant incubator: what are their differences?

An infant warmer is specialized equipment used to provide newborns with a comfortable warming area that maintains their body temperature at 36 to 37 degrees, thus providing a warm and cozy environment that helps them maintain their body temperature.
When should a child radiant heater be used?
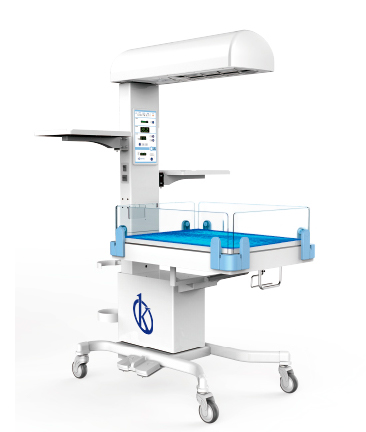
The usefulness of this equipment highlights in its 4 main functions of rescue and integral management in the newborn, is a unit that guarantees the effective flow of work, favors the immediate attention of medical personnel belonging to emergencies, in addition to reducing the time of rescue and immediate and detailed care of the newborn, radiant infant heaters, are primarily used in the delivery rooms, neonatal care, neonatal intensive care, areas of neonatal intensive therapy, and in the pre and postoperative care of the newborn.
Infant radiant heater: When is it necessary?
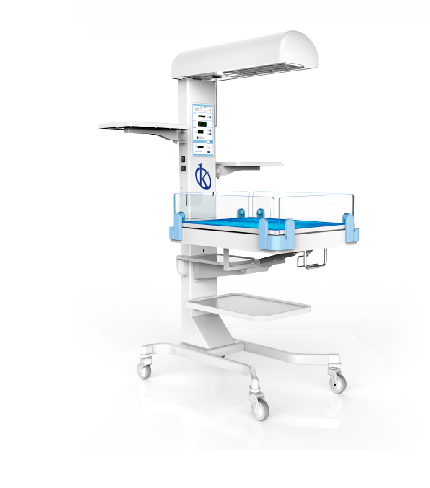
An infant radiant warmer is medical equipment used in neonatal intensive care units, aimed at providing the newborn with a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature within normal levels. This is because when a baby is born from the mother’s womb, which is a natural incubator, it needs to be heated.
Children’s radiant heater: When should it be used?

A radiant infant heater is a medical equipment used in the field of neonatology and pediatrics, specifically in neonatal intensive care units, to provide newborns with a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees.
Is a child radiant heater important?

A child radiant heater is a unit used to provide radiant heat to newborns in a comfortable thermal area that maintains their body temperature from 36 to 37 degrees. Newborns who are placed in radiant heaters are usually premature or low birth weight patients who have thermo-regulation problems and are therefore unable to maintain thermal balance, and newborns who may present some critical condition that require constant intervention by medical personnel.
